Radiation and outflow properties of super-Eddington accretion flows around various mass classes of black holes: Dependence on the accretion rates
Yoshioka, Shogo, Mineshige, Shin, Ohsuga, Ken, Kawashima, Tomohisa, & Kitaki, Takaaki
要旨
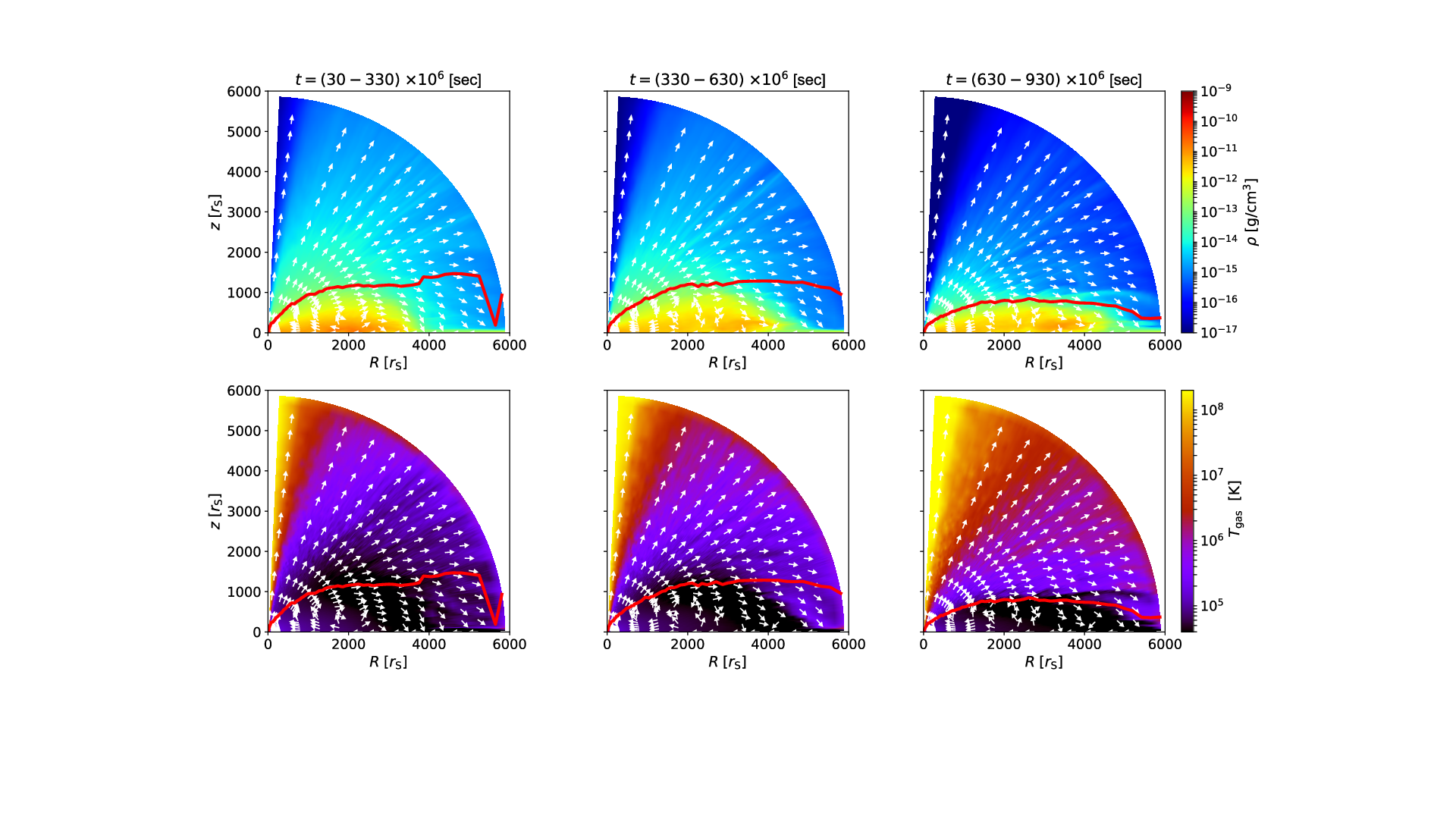
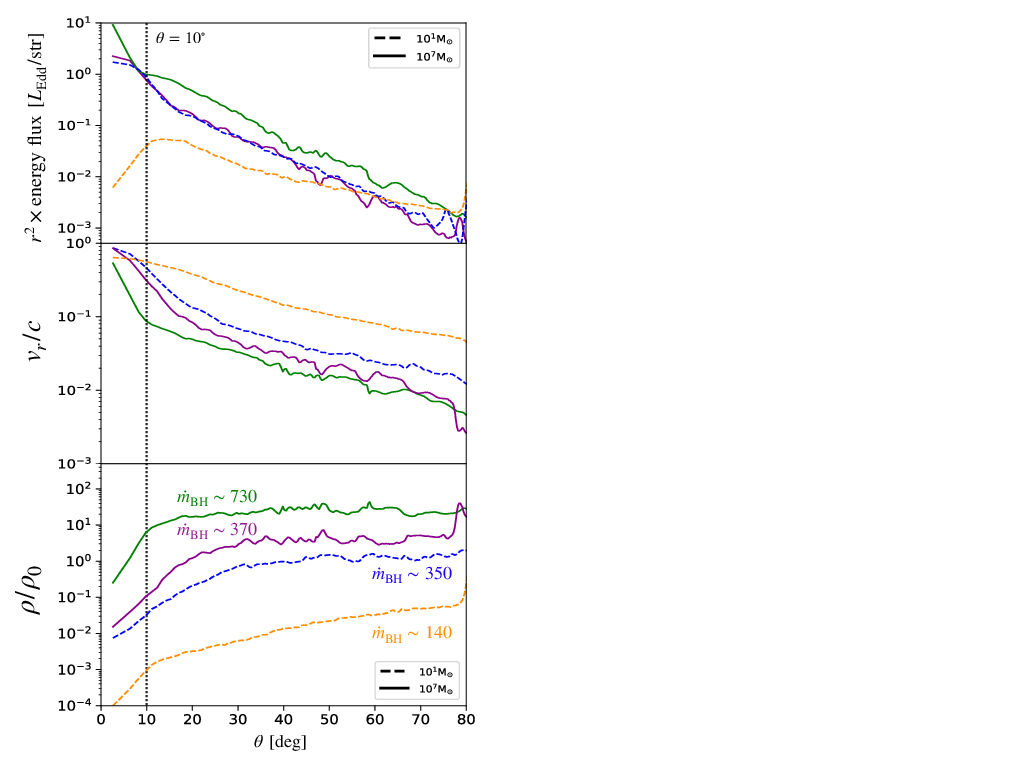
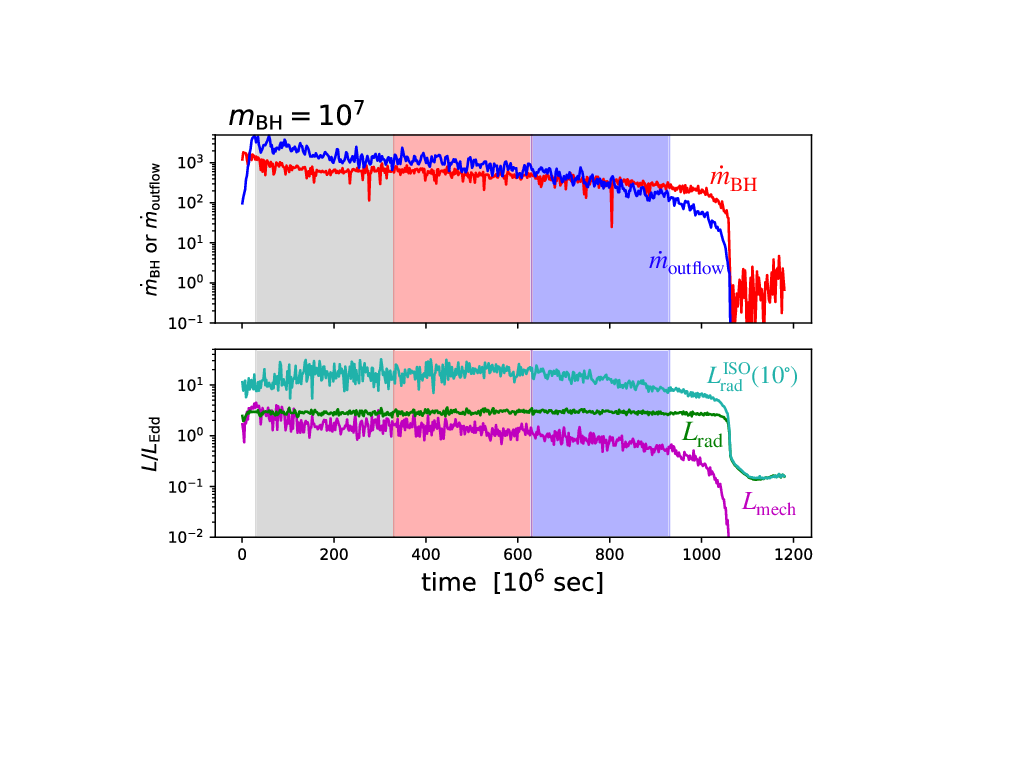
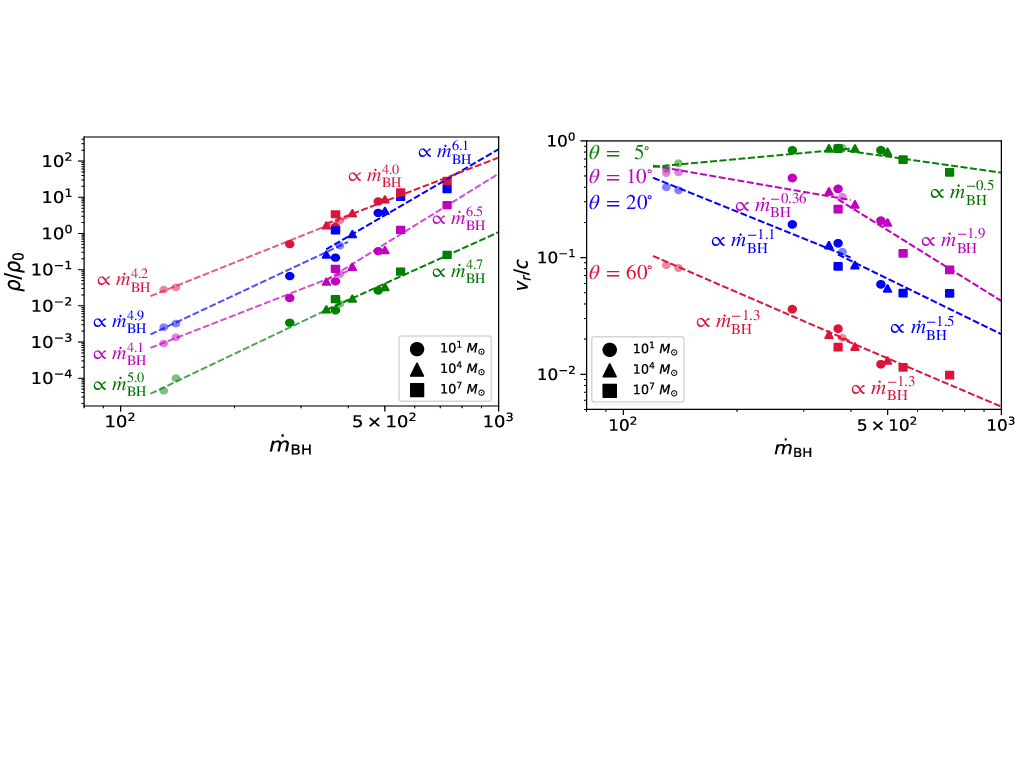
We perform axisymmetric two-dimensional radiation-hydrodynamic simulations of super-Eddington accretion flow and outflow around black holes to examine the properties of radiation and outflow as functions of the black hole mass and the accretion rate on to the black hole (ṀBH). We find that the ṁBH(≡ṀBHc2∕LEdd) dependence of Lrad∕LEdd and Lmech∕LEdd found for a stellar-mass black hole can apply to the high-mass cases, where Lrad is the radiation luminosity, Lmech is the mechanical luminosity, c is the speed of light, and LEdd is the Eddington luminosity. Such universalities can appear in the regime in which electron scattering opacity dominates over absorption opacity. Further, the normalized isotropic mechanical luminosity LmechISO∕LEdd (evaluated by normalized density and velocity at θ = 10∘) exhibits a broken power- law relationship with ṁBH; LmechISO∕LEdd ∝ṁBH2.7 (or ∝ṁBH0.7) below (above) ṁBH ~ 400. This is because the radial velocity stays nearly constant (or even decreases) below (above) the break with increase of ṁBH. We also find that the luminosity ratio is Lmech∕LradISO ~ 0.05 at ṁBH ~ 100, which is roughly consistent with the observations of NLS1, 1H 0323+103.



 Ja En
Ja En