About Us

Our group strives to uncover the basic physics of star formation, planetary systems, active galactic nuclei, the birth of stars and galaxies of the early universe, the characteristics of the light they emit, formation and evolution of galaxies and black holes. We tackle many of the problems of modern astrophysics by solving equations of relativistic radiation hydrodynamics, radiation transport, and gravitational dynamics, which faithfully capture the interaction of light with matter and the complex gravitational interactions, so crucial in the study of the formation and evolution of stars, galaxies, and black holes. To find solutions to the complicated system of equations that describe multi-component celestial bodies and turbulent flow, we conduct large-scale numerical simulations, using, amongst others, tailor-made supercomputers at the Center for Computational Sciences.
Featured Articles
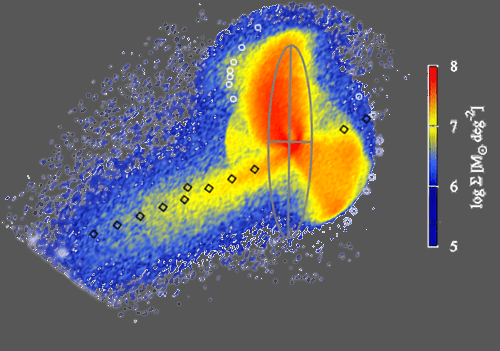
Simultaneous Formation of the Andromeda Giant Southern Stream and the Substructures in the Andromeda Halo
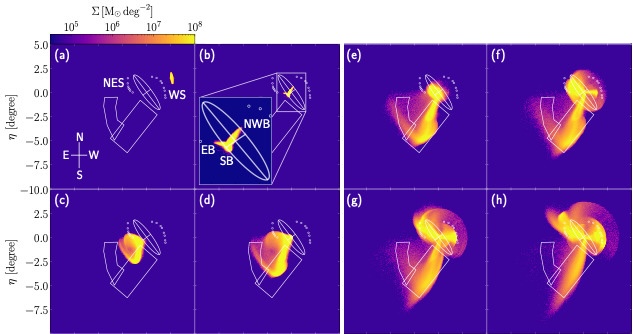
The Cold Dark Matter (CDM) model, the current standard model of structure formation, suggests that larger galaxies formed hierarchically through the collisions and mergers of dwarf galaxies. Theory predicts that during this process, diffuse, faint structures consisting of stars, known as stellar streams (elongated stellar populations), emerge in the halo...
Recent Posts
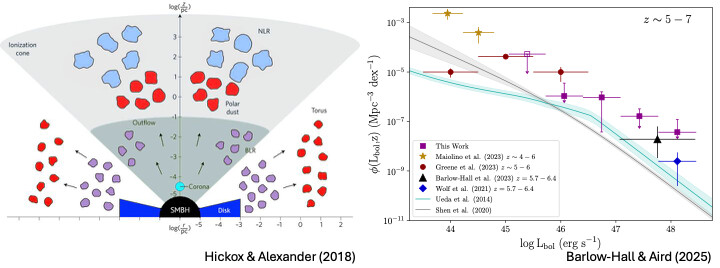
X-ray AGN in the High Redshift Universe
Cassandra Barlow-Hall
Among the most energetic processes in the Universe, Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) have been found throughout cosmic history; powered by a central Supermassive Black Hole (SMBH) with those at $z\gtrsim6$ being comparable in mass to SMBHs at $z\sim1$. The formation mechanism of SMBHs remains the subject of much debate, yet AGN are thought to have intrinsic links to the growth of their host galaxies. Understanding the rapid mass growth of SMBHs that must be occurring during this epoch—and crucially their impact on host galaxies—is vital to our understanding of the early Universe. X-rays are often used as a principal tracer...

Professor Ken Ohsuga wins best faculty award 2024
Professor Ken Ohsuga, head of our group, has won the University of Tsukuba 2024 Best Faculty Member...

Students in our group win awards!
This year, we had several students win awards: 校友会江崎賞:Erika Ogata 数理物質科学研究群長賞:Erika Ogata 物理学学位プログラムリーダー賞:Takuhiro Yuasa 学生表彰(学長表彰):Michi Shinozaki 卒研ベストプレゼンテーション賞:Shinozaki...

Associate Professor Hidenobu Yajima wins best faculty award 2022
Associate Professor Hidenobu Yajima has won the University of Tsukuba 2022 Best Faculty Member award! The award...
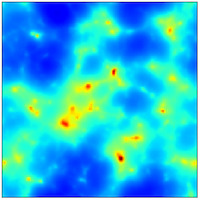
[Press release] The Cosmic Neutrino Background: World's First Six-dimensional Simulations
In this research, we solved the Vlasov-Poisson equations directly by running our new high-precision numerical scheme for...
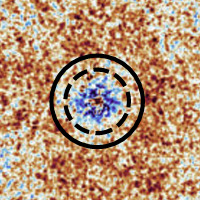
Connecting high-redshift galaxies and the intergalactic medium
Recent work has suggested that, during reionisation, spatial variations in the ionising radiation field should produce enhanced...
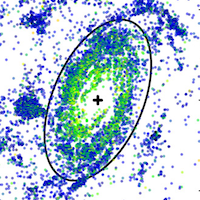
Galaxy archaeology through the synergy of Subaru and space telescopes
Over the last two decades, wide-field resolved star studies have shown a remarkable variety of stellar (sub-)structures...
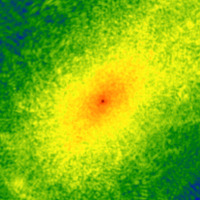
Probing the quantum-like nature of the dark matter using observations of dwarf...
Satellite abundance in Milky Way-like halos plays a crucial role in distinguishing dark matter models, in particular,...
Mapping the High-Redshift Universe Across Scales with the Lyman-alpha line
The Lyman-alpha emission line offers a powerful window into galaxies and their diffuse environments at high redshift....

The Cosmic Himalayas; An Extreme Quasar Concentration at Cosmic Noon Bridging AGNs,...
Roughly 10 billion years ago, during the Universe’s most active phase of star formation and black hole...
Ionization Environment in Star-Forming Galaxies during the Epoch of Reionization
ALMA and JWST have been pushing up the redshift frontier to z~14 and pioneering metal emission line...

Looking for black holes through peculiar molecular clouds in the galactic center...
The region within a radius of approximately 200 parsecs from the Galactic Center is known as the...
Dark matter signatures in/from the Universe
Dark matter (DM) is a mysterious energy component of our Universe which occupies about a quarter of...

Formation of Astrophysical Objects 2025
This workshop aims to provide an opportunity to exchange views and share information about the current status...

Formation of Astrophysical Objects 2024
This workshop aims to provide an opportunity to exchange views and share information about the current status...

The grand meeting on black holes
~from stellar mass to super massive...
Almost 100 years after the prediction of general relativity, the existence of black holes has finally been...

Formation of Astrophysical Objects 2023
This workshop aims to provide an opportunity to exchange views and share information about the current status...
Recent Work
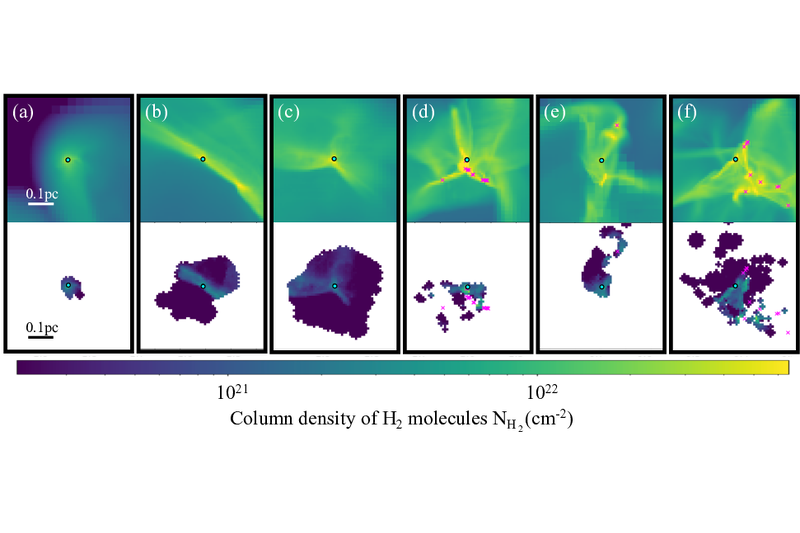
Tracking Star-forming Cores as Mass Reservoirs in Clustered and Isolated Regions Using Numerical Passive Tracer Particles
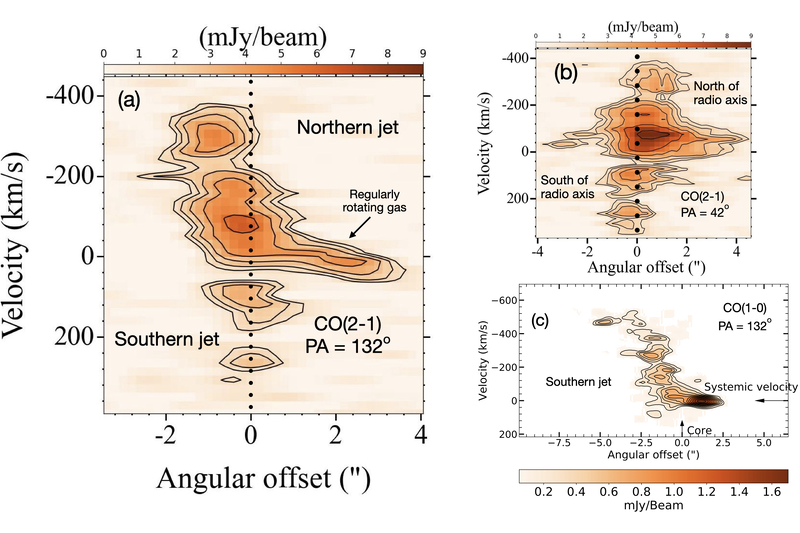
Cold gas bubble inflated by a low-luminosity radio jet
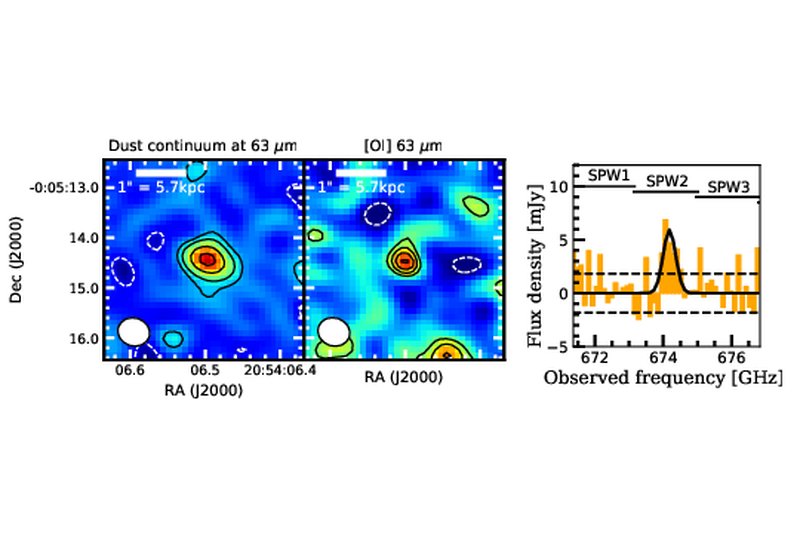
Detection of the [O I] 63 μm emission line from the z = 6.04 quasar J2054-0005
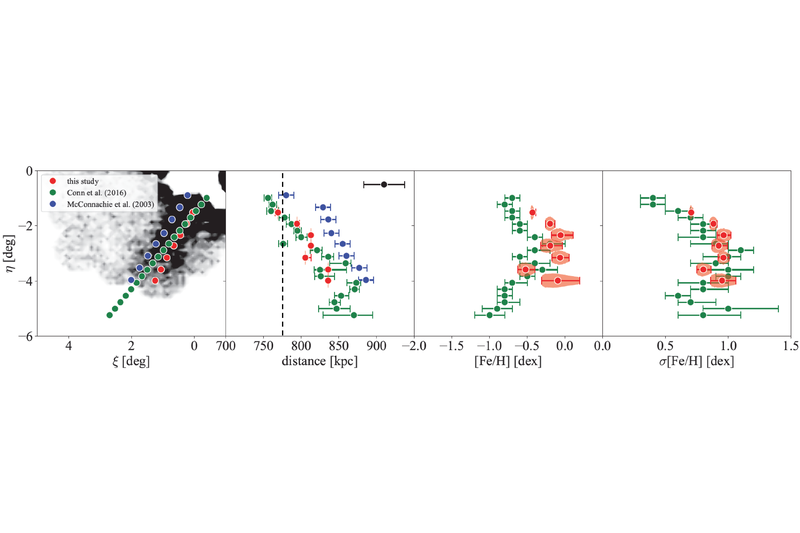
The structure of the stellar halo of the Andromeda galaxy explored with the NB515 for Subaru/HSC - I. New insights on the stellar halo up to 120 kpc
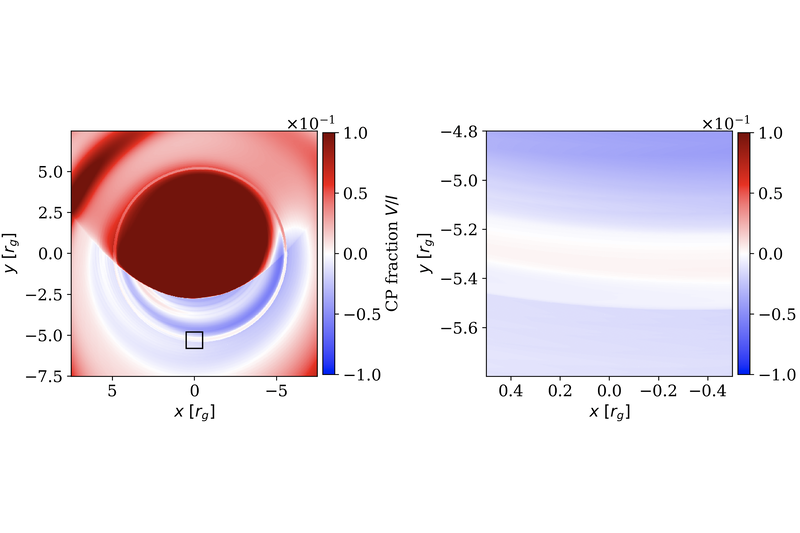
Survey of non-thermal electrons around supermassive black holes through polarization flips
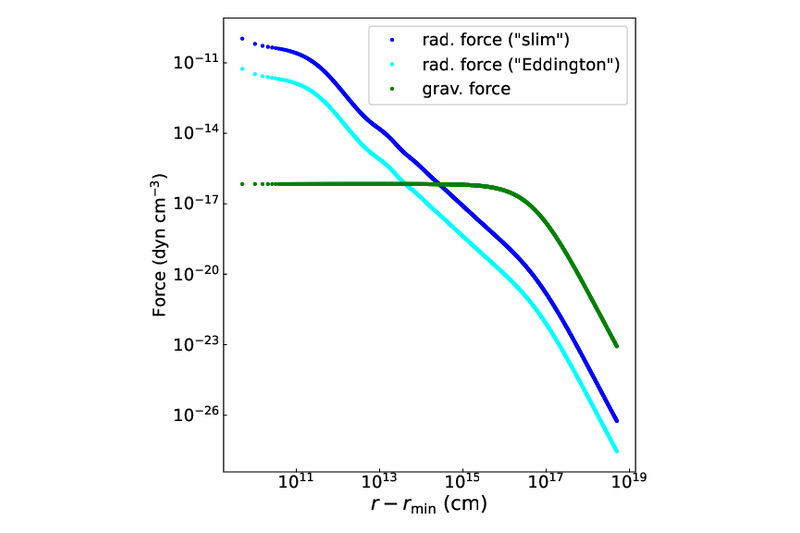
Impact of the Lyα radiation force on super-Eddington accretion on to a massive black hole

 和 英
和 英