Research Projects
Development of the general relativistic radiation magneto-hydrodynamic code Inazuma
To predict the gas dynamics around a black hole, we need to perform calculations that incorporate general relativity, magnetohydrodynamics, and radiation transport, that is, general relativistic radiation magnetohydrodynamics (GR-RMHD) calculations. The only way to solve this problem is numerically using a supercomputer. To this end, we developed the world's first GR-RMHD simulation code, UWABAMI, a GR-RMHD code with which we began performing production runs in 2015 and which achieved tremendous success, yielding models of high-luminosity black hole accretion disks and radiation-driven jets. Recently, we completed the development of the GR-RMHD code, INAZUMA, which solves the radiation field even more accurately, and with which we shall begin production runs soon. In order to minimize numerical dispersion of the radiation, a method for solving radiation transport equations along geodesics (based on the ARTIST code) is planned for future implementation.
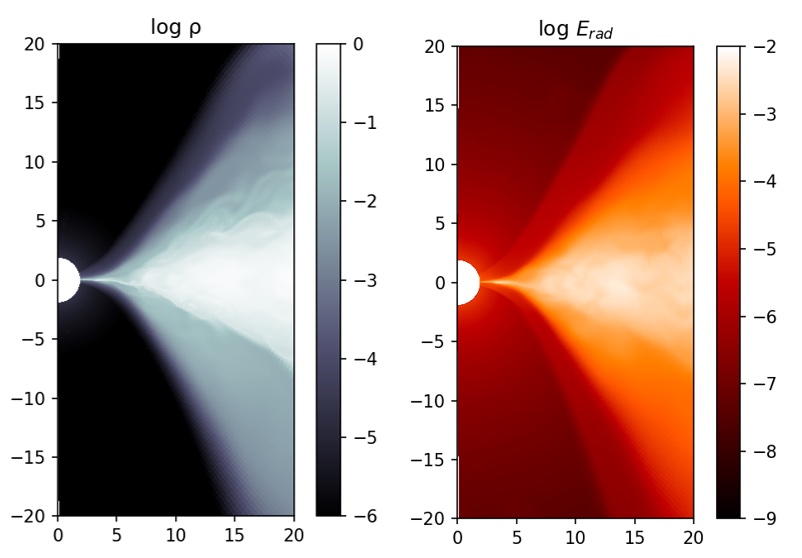
Fig. 1 Maps of the black hole accretion disc and jet from general relativistic radiation magnetohydrodynamics calculations with the INAZUMA code. Left: density distribution; Right: the energy density distribution of radiation.

 和 英
和 英