Achievements & Publications
An Unbiased CO Survey Toward the Northern Region of the Small Magellanic Cloud with the Atacama Compact Array. II. CO Cloud Catalog
Ohno, Takahiro, Tokuda, Kazuki, Konishi, Ayu, Matsumoto, Takeru, Sewiło, Marta, Kondo, Hiroshi, Sano, Hidetoshi, Tsuge, Kisetsu, Zahorecz, Sarolta, Goto, Nao, Neelamkodan, Naslim, Wong, Tony, Fukushima, Hajime, Takekoshi, Tatsuya, Muraoka, Kazuyuki, Kawamura, Akiko, Tachihara, Kengo, Fukui, Yasuo, & Onishi, Toshikazu
Abstract
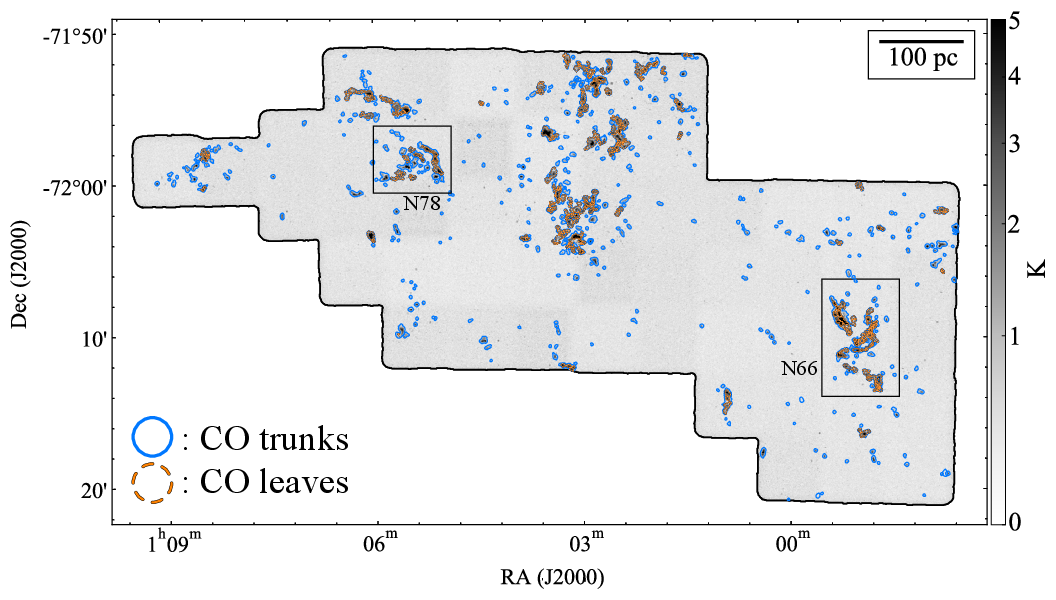
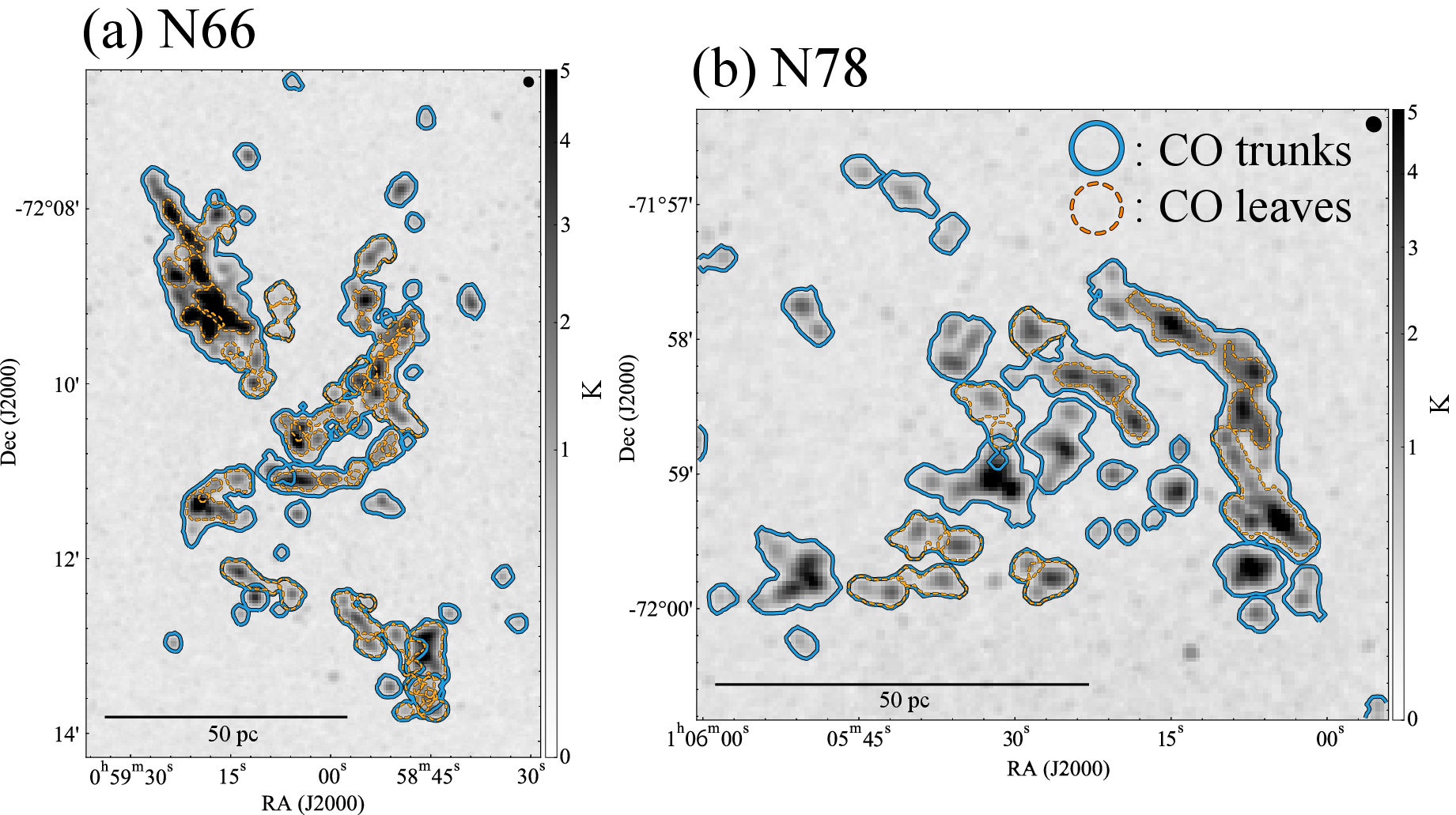
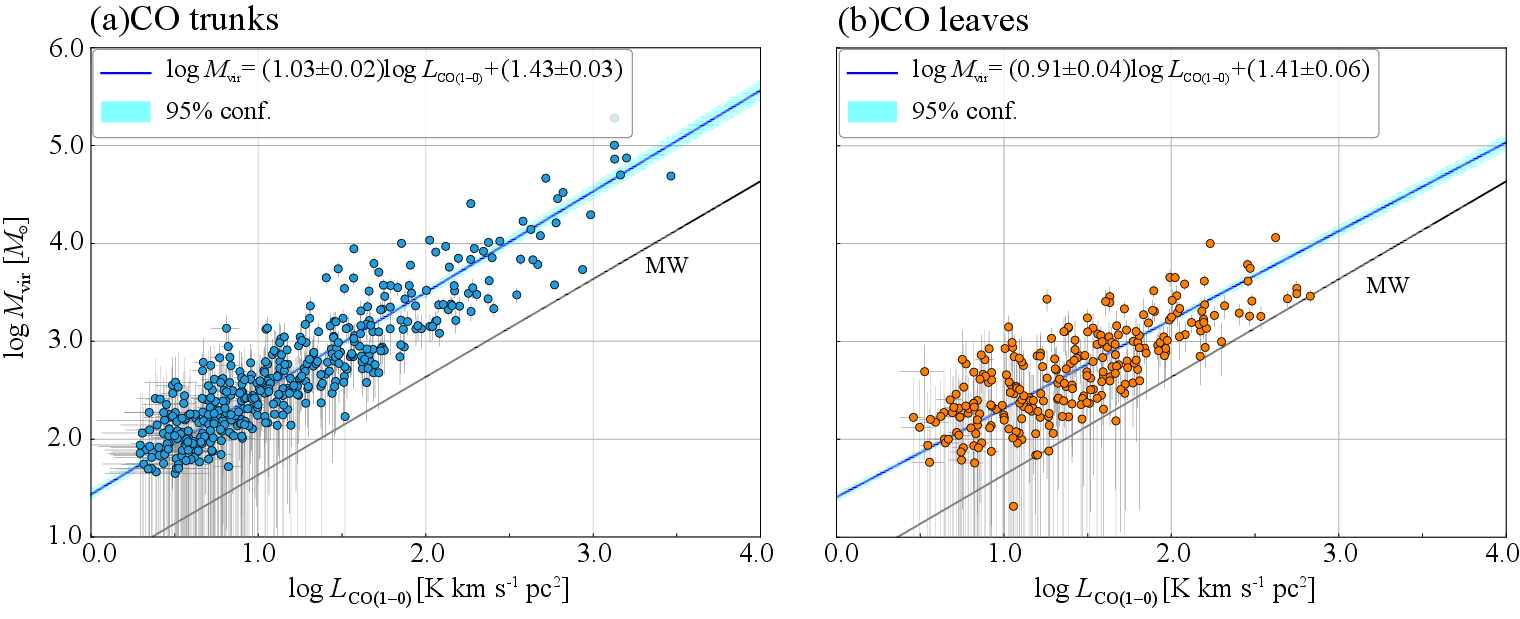
The nature of molecular clouds and their statistical behavior in subsolar metallicity environments are not fully explored yet. We analyzed data from an unbiased CO (J = 2-1) survey at the spatial resolution of ~ 2 pc in the northern region of the Small Magellanic Cloud with the Atacama Compact Array to characterize the CO cloud properties. A cloud-decomposition analysis identified 426 spatially/velocity- independent CO clouds and their substructures. Based on the cross-matching with known infrared catalogs by Spitzer and Herschel, more than 90% CO clouds show spatial correlations with point sources. We investigated the basic properties of the CO clouds and found that the radius-velocity linewidth (R-σ v) relation follows the Milky Way-like power-law exponent, but the intercept is ~ 1.5 times lower than that in the Milky Way. The mass functions (dN/dM) of the CO luminosity and virial mass are characterized by an exponent of ~ 1.7, which is consistent with previously reported values in the Large Magellanic Cloud and in the Milky Way.


 和 英
和 英