FOREVER22: galaxy formation in protocluster regions
Yajima, Hidenobu, Abe, Makito, Khochfar, Sadegh, Nagamine, Kentaro, Inoue, Akio K., Kodama, Tadayuki
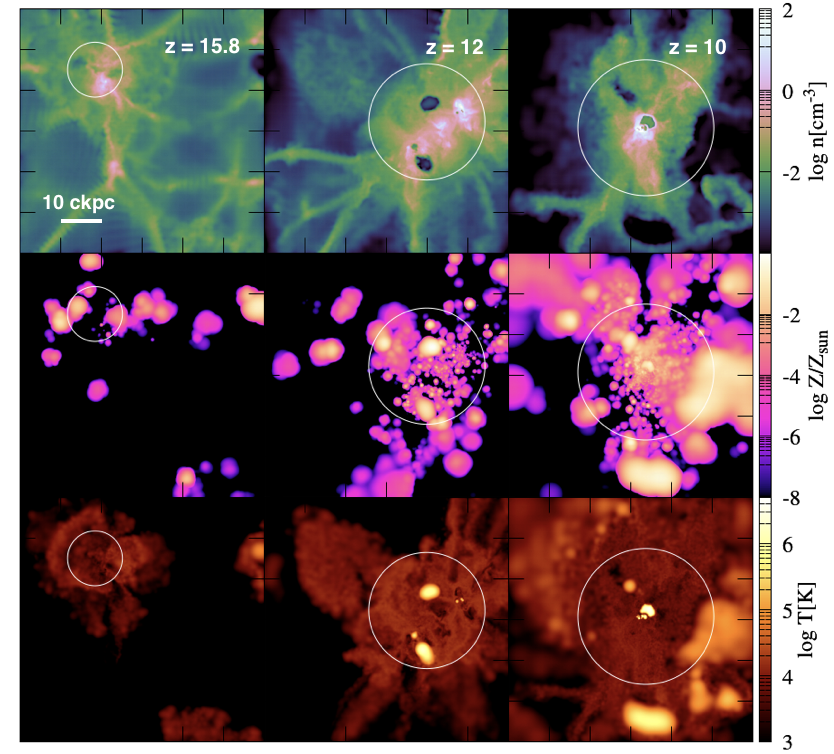
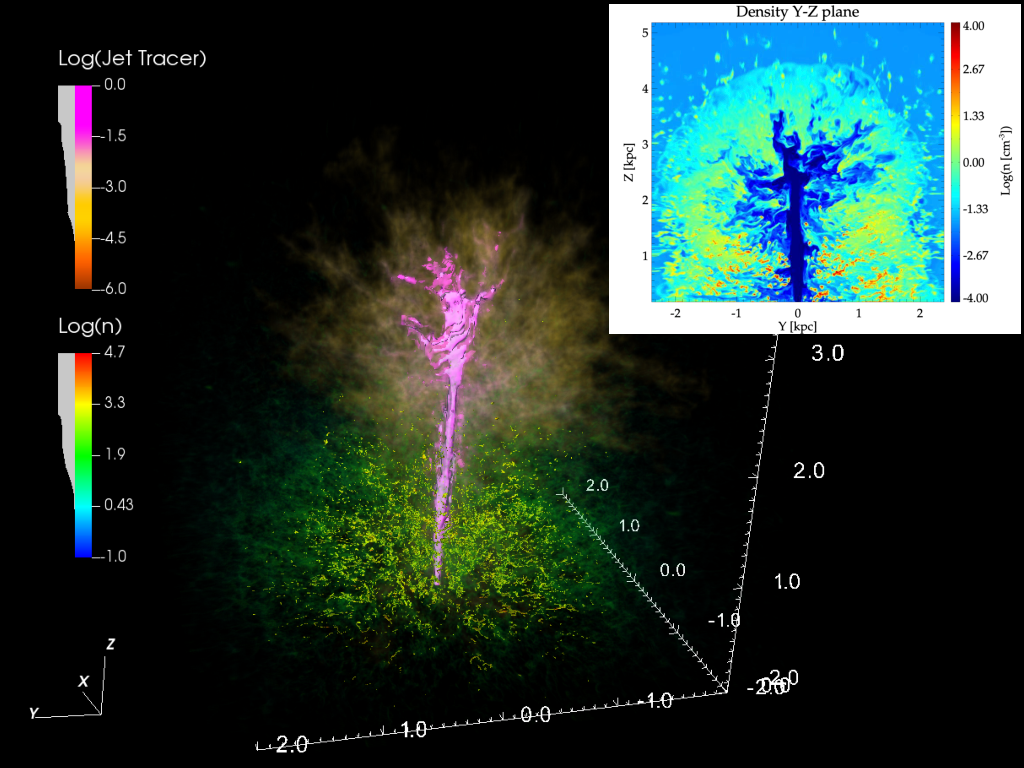
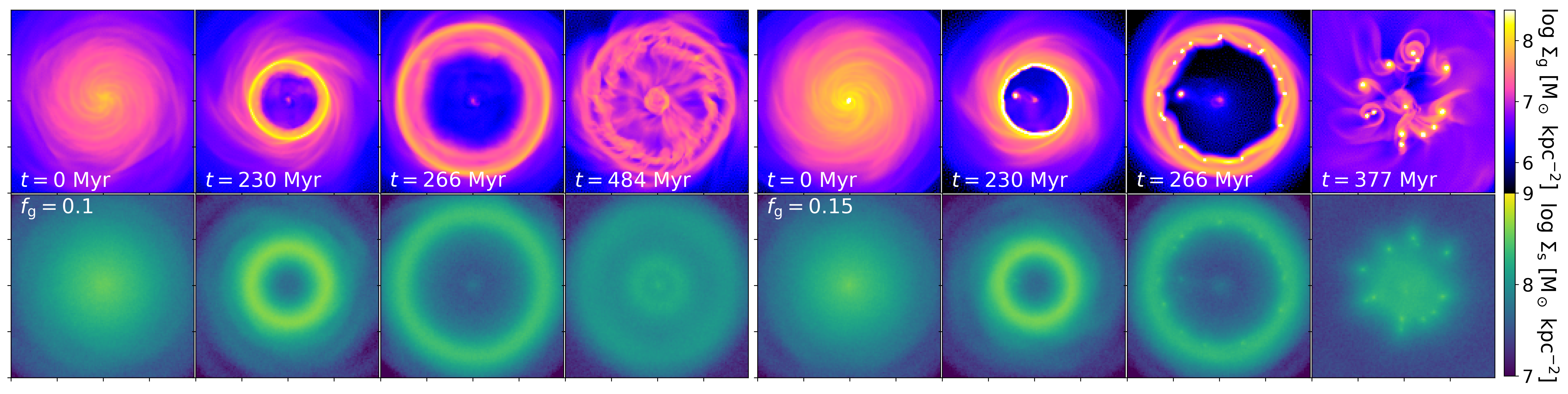
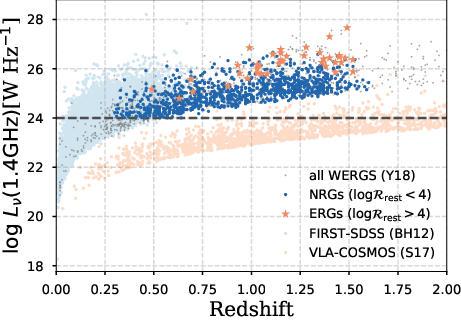
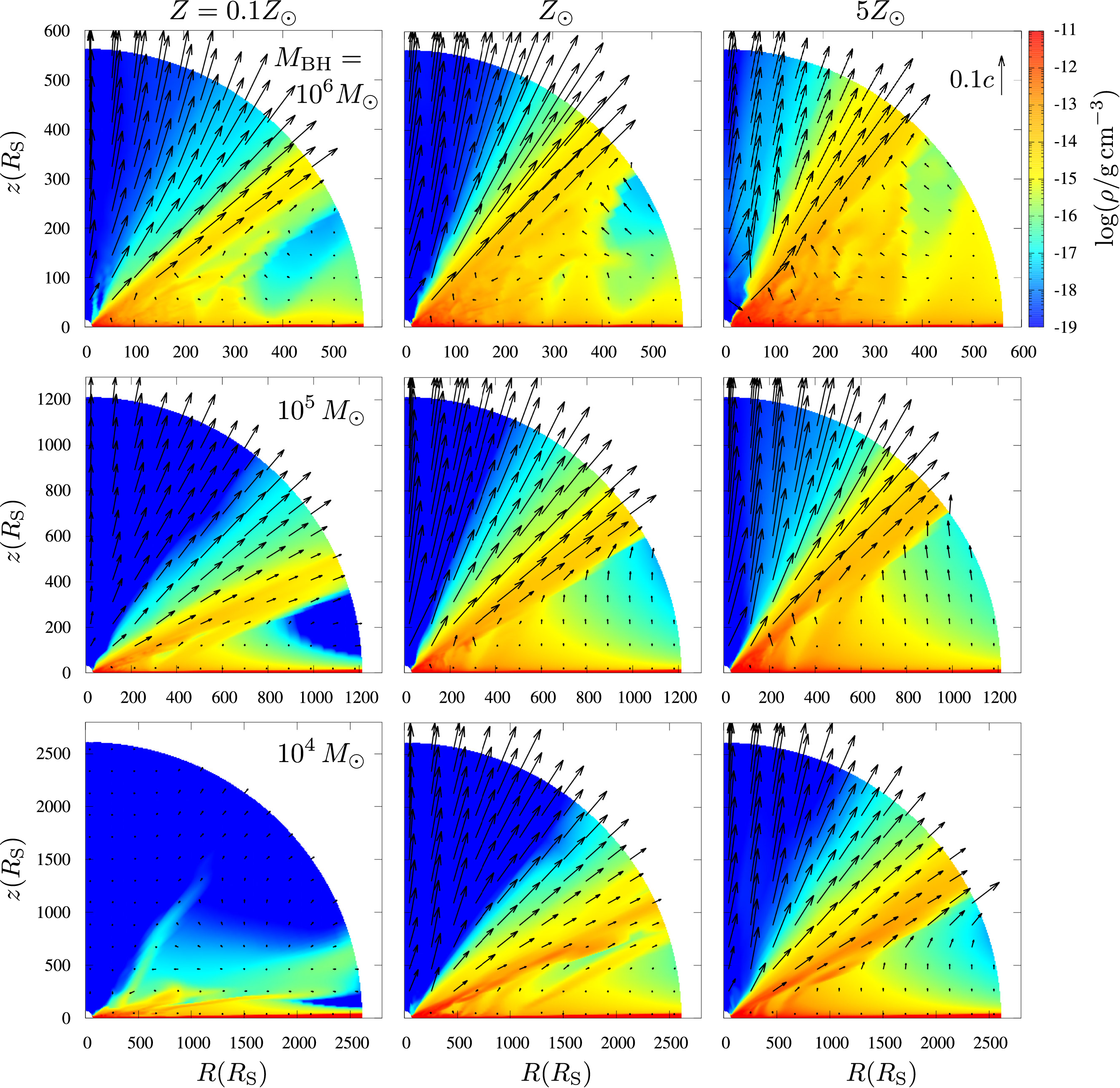
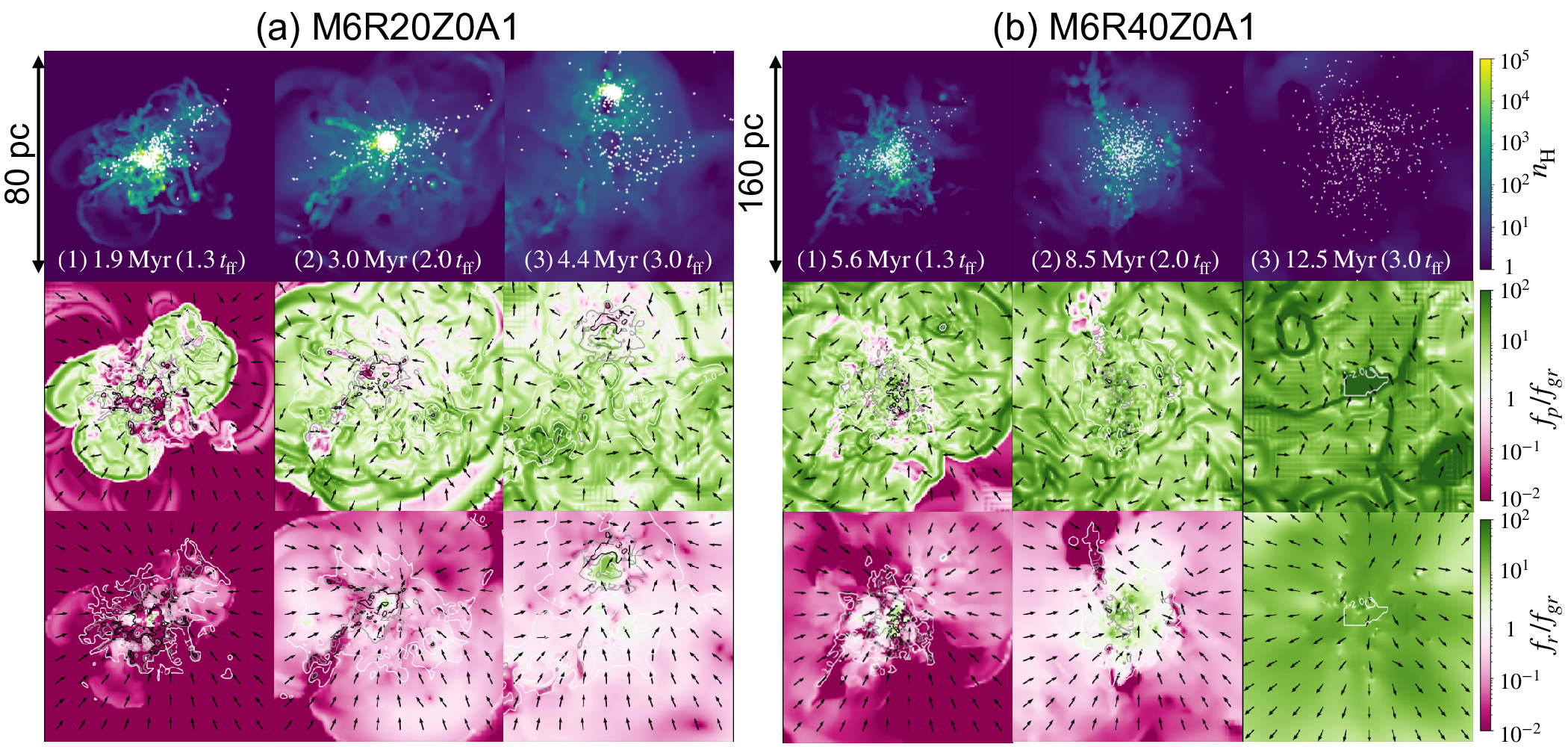
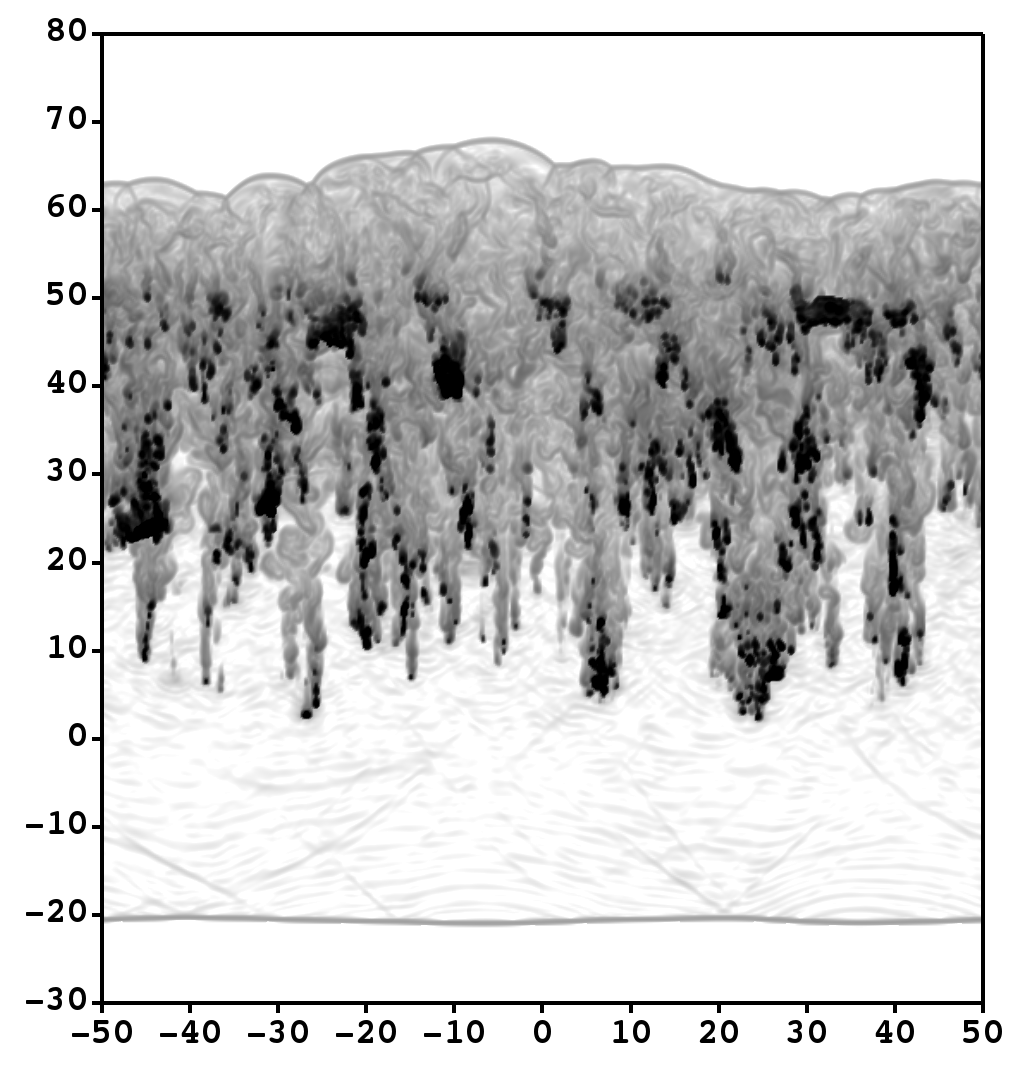
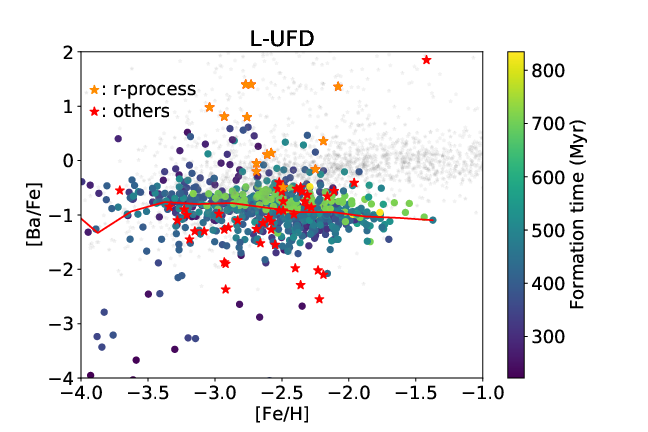
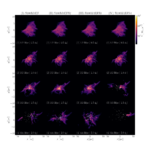
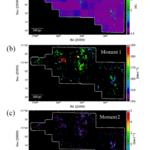
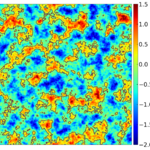
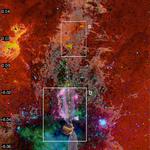
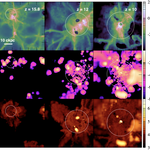
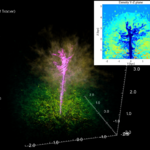
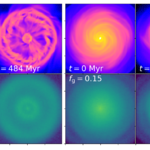
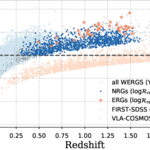
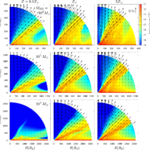
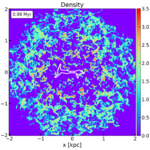
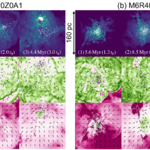
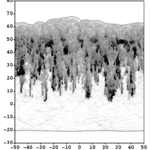
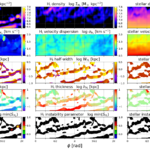
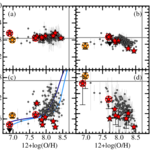
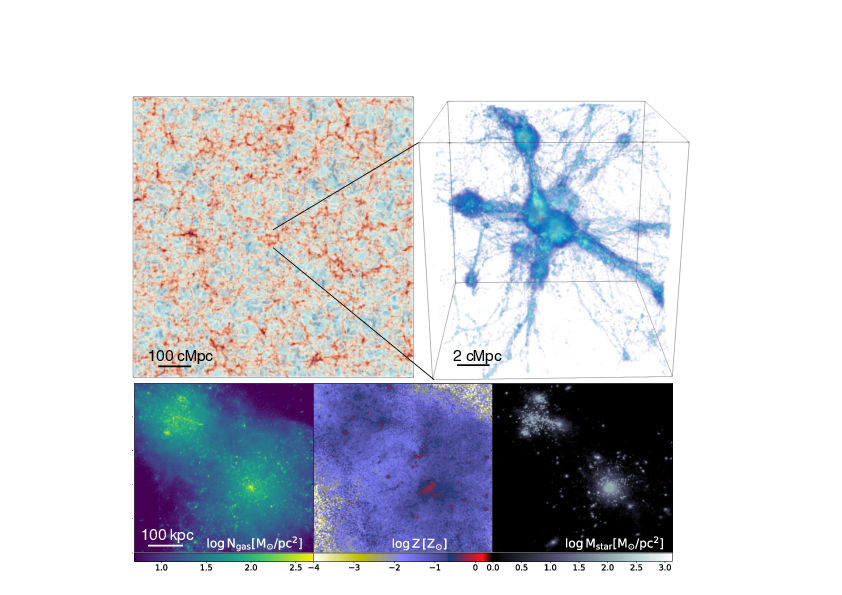
We present results from a new cosmological hydrodynamics simulation campaign of protocluster (PC) regions, FOREVER22: FORmation and EVolution of galaxies in Extremely overdense Regions motivated by SSA22. The simulations cover a wide range of cosmological scales using three different zoom set-ups in a parent volume of (714.2 cMpc)3: PCR (Proto-Cluster Region;...

 和 英
和 英