Achievements & Publications
Structure of the super-Eddington outflow and its impact on the cosmological scale
Botella, Ignacio, Mineshige, Shin, Kitaki, Takaaki, Ohsuga, Ken, & Kawashima, Tomohisa
Abstract
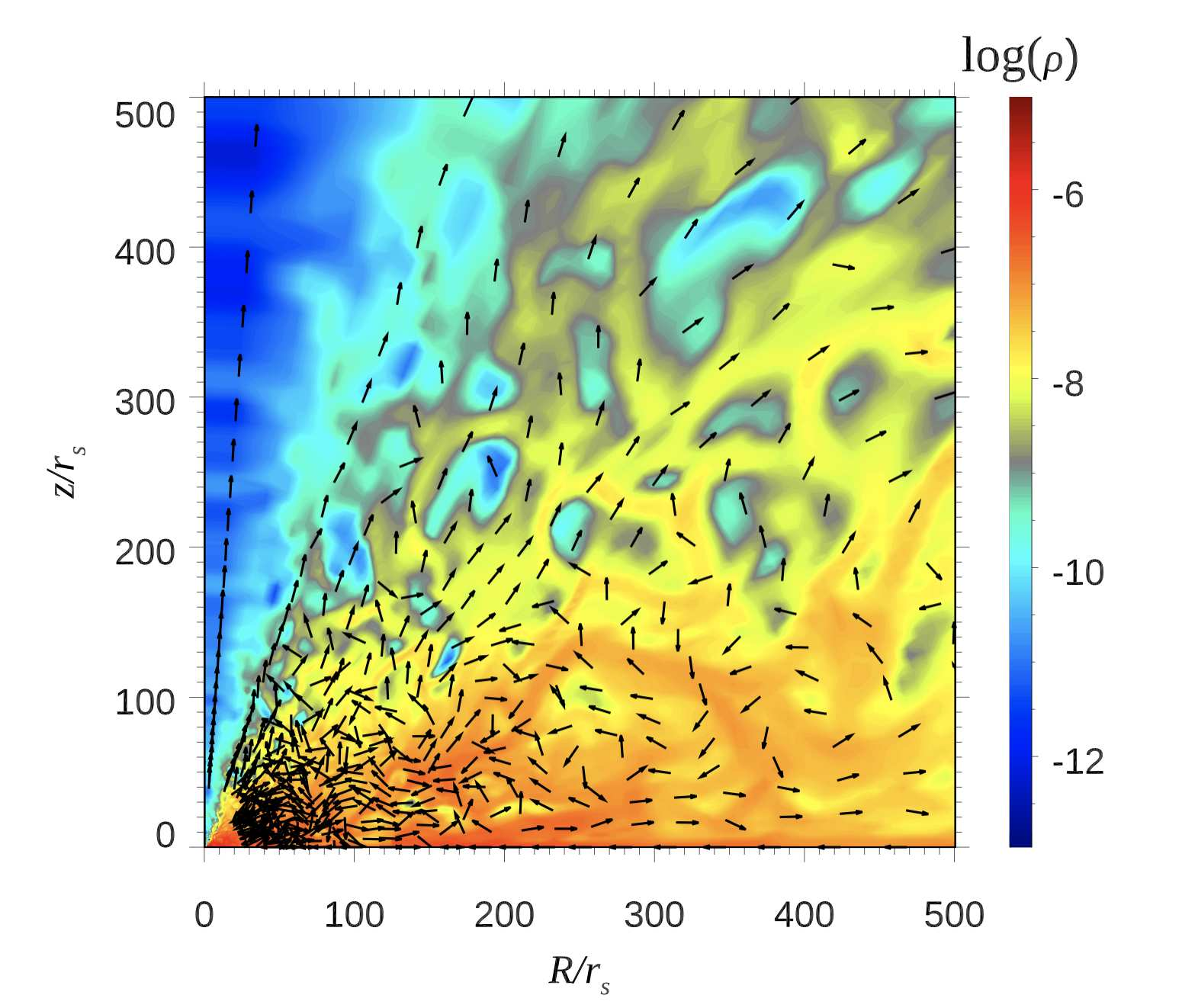
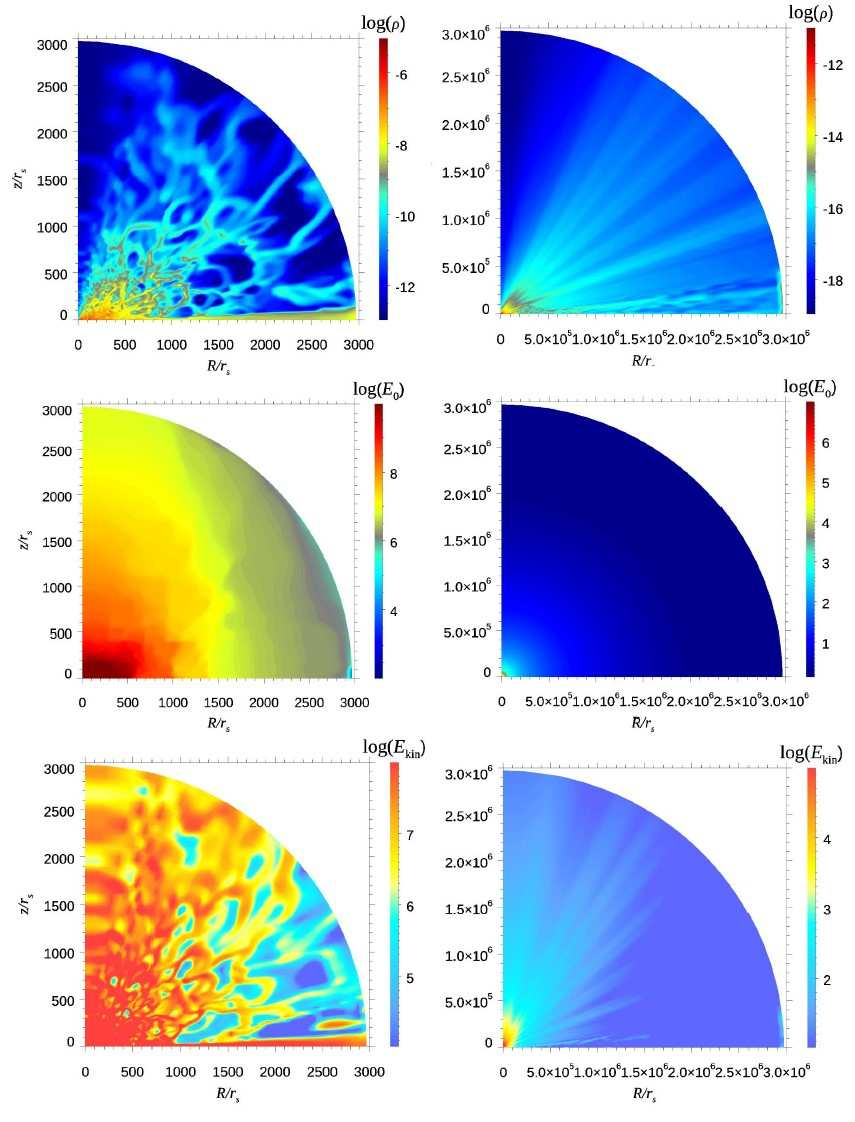
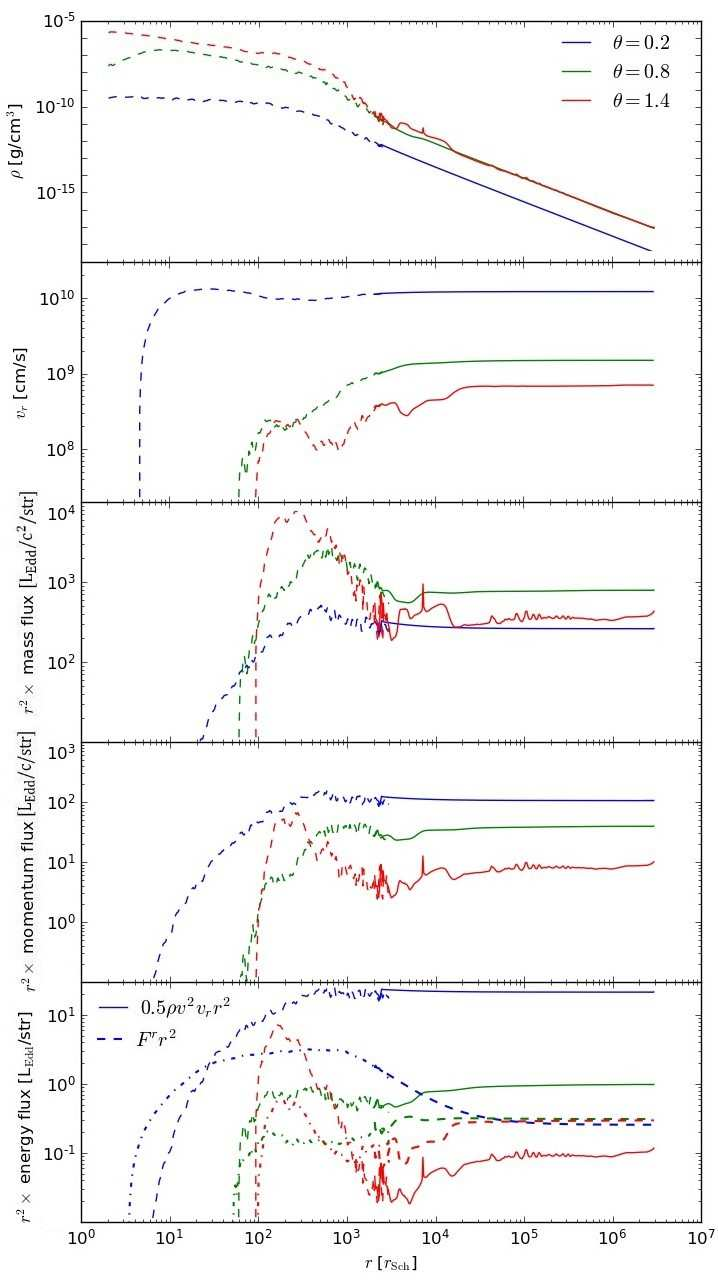
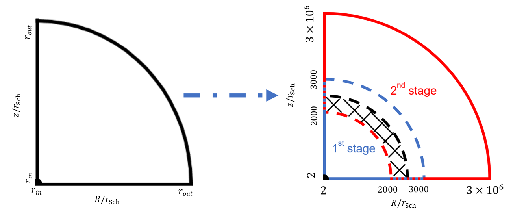
It is one of the biggest issues in black hole (BH) astrophysics how to evaluate BH feedback to its environments precisely. Aiming at studying the unique gas dynamics of super-Eddington flow around supermassive black hole (SMBH) seeds at high redshift, we carried out axisymmetric two-dimensional radiation hydrodynamic simulations using a nested simulation-box method. Here we divide the simulation box into an inner zone at (2-3 × 103)rSch (with rSch being the Schwarzschild radius) and an outer zone at (2 × 103-3 × 106)rSch, with smooth connection of the physical quantities, such as gas density, velocity, and radiation energy. We start the calculation by injecting mass through the outer boundary of the inner zone at a constant rate of Ṁinj = 103LEdd∕c2, where LEdd is the Eddington luminosity and c is the speed of light. A powerful outflow is generated in the innermost region and it propagates from the inner zone to the outer zone. The outflows are characterized by a velocity of 0.02c (0.7c) and density of 10-17 (10-19) g cm-3 for near the edge-on (face- on) direction. The outflow is gradually accelerated as it travels by accepting radiation-pressure force. The final mass outflow rate at the outermost boundary is Ṁout ~ 0.3 ×Ṁinj. By extrapolating the outflow structure to a further larger scale, we find that the momentum and energy fluxes at r ~0.1 pc are ~10-100 LEdd/c and ~0.1-10 LEdd, respectively. Moreover, we find that the impacts are highly anisotropic, in the sense that larger impacts occur towards the face-on direction than in the edge-on direction. These results indicate that the BH feedback will work more efficiently on the interstellar medium than assumed in the cosmological simulations.

 和 英
和 英