SSH (secure shell) is a common method for using remote machines. In this section, we explain execution of OmniRPC applications using ssh. In addition, like using Globus, create a remote executable module, register a program, and to create program are almost the same. The only different details is the description of hostfile (hosts.xml).
In this example, the environment is described below.
We assume that we can use SSH here. That is, we assume that we can access with SSH from alice.hpcs.is.tsukuba.ac.jp to dennis.hpcc.jp.
When using SSH, you should set up auto authentication with an ssh-agent. If you do not, you have to type in the password at each remote host. If you want to know more detail, see man of "ssh-agent", In this example, we outline the usage below.
$ eval `ssh-agent`
$ ssh-add type your pass phrase here. Identity added: /home/msato/.ssh/id_rsa (/home/msato/.ssh/id_rsa) $
With the above procedure, you should confirm whether auto authentication is running or not.
$ ssh dennis.hpcc.jp
With the above command, you can login to remote hosts without typing the password.
To use dennis.hpcc.jp, you should describe hosts.xml, and execute the client program with this hostfile. Write the hostfile for using ssh, as follows.
<?xml version="1.0" ?> <OmniRpcConfig> <Host name="dennis.hpcc.jp" arch="i386" os="linux"> <Agent invoker="ssh" /> </Host> </OmniRpcConfig>
This description is for activating the agent with ssh. In this specification, the relationship between the agent and rex is shown below.
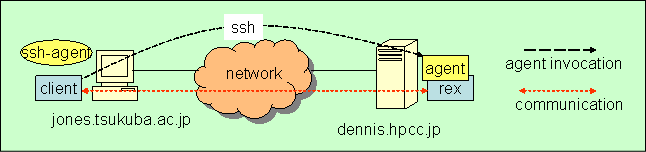
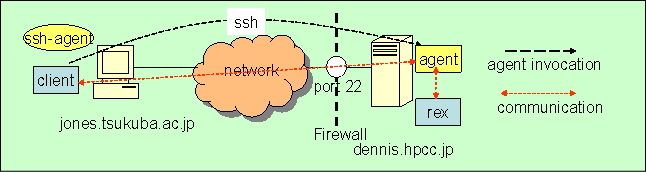
There will be some firewalls between remote hosts and the client host when the client host and the remote hosts extend across administrations. When we use ssh for agent activation, programs communicate with the client and agent, using ssh port forwarding. Using the ssh port forwarding function, we can communicate between remote executable modules on the remote host and client program. This is OmniRPC's multiplex communication function. If you want to use this feature, specify the "mxio" attribution in the agent.
<?xml version="1.0" ?> <OmniRpcConfig> <Host name="dennis.hpcc.jp" arch="i386" os="linux"> <Agent invoker="ssh" mxio="on" /> </Host> </OmniRpcConfig>
the relationship of the agent and rex with this option is as follows. In this case, communication with rex and the client program occurs by way of rex.
You can execute in same manner without using hosts.xml.
% a.out --hostfile hosts.xml args ...
In addition, if the user name is different on client host and remote host, describe hostfile.xml as follows.
<?xml version="1.0" ?> <OmniRpcConfig> <Host name="dennis.hpcc.jp" user="msato" arch="i386" os="linux"> <Agent invoker="ssh" mxio="on" /> </Host> </OmniRpcConfig>